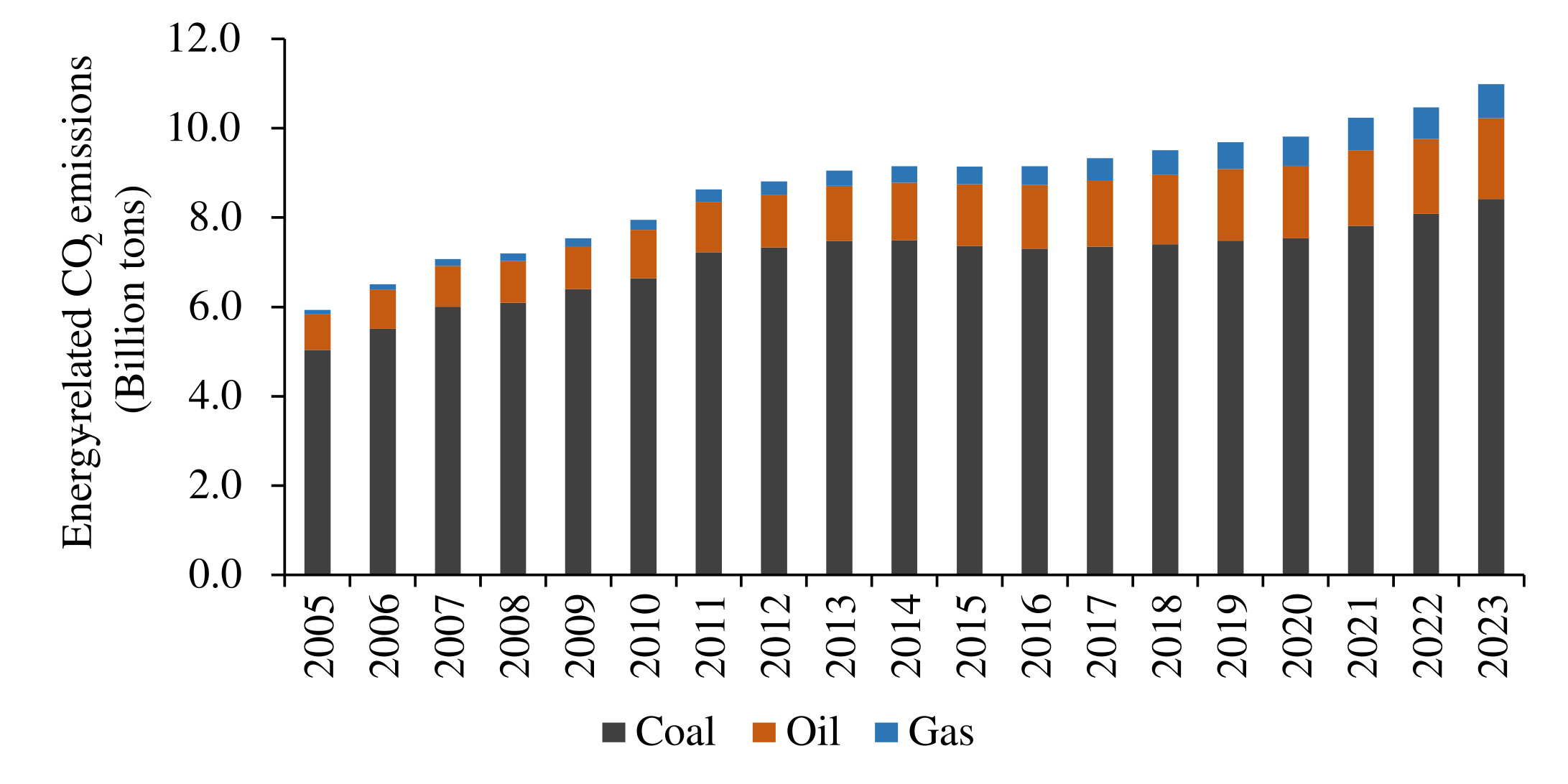
Beijing, (SONNA): — As the climate crisis intensifies, and the world grapples with droughts, floods, wildfires, and record-breaking heatwaves, one country is quietly but steadily rewriting the global script on climate leadership. For years, China was viewed primarily as the world’s largest emitter, a nation powered by coal and rapid industrial expansion. Today, that narrative is shifting. In a sweeping effort that blends ambition, pragmatism, and technology, China is building the foundations of a greener future not just for itself, but for the world.
The urgency is clear. A child born in 2020 is expected to face up to six times more droughts and 36 times more heatwaves in their lifetime, according to Science magazine. In cities like Shanghai, rising sea levels are no longer theoretical threats, they are approaching realities. China, recognizing both its responsibility and vulnerability, has committed to peak carbon emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. These goals, once met with skepticism, are now being backed by concrete progress on a scale unmatched anywhere else in the world.
Nowhere is this more evident than in China’s renewable energy transformation. In the past few years, the country has emerged as the undisputed global leader in wind and solar power. Vast solar farms now glisten across the deserts of Gansu and Xinjiang, while offshore and inland wind turbines rise across the skyline like modern monuments to a new era. In 2022 alone, China added more renewable energy capacity than the rest of the world combined, a staggering feat that underscores not just its determination, but its ability to act swiftly and at scale.
“China’s renewable boom isn’t just about size, it’s about speed and coordination,” says Professor Yazhen Gong, an environmental economist at Renmin University of China. “They are showing that economic growth and environmental responsibility can be aligned. And they’re doing it without waiting for global consensus.”
But China’s approach to climate action goes beyond building infrastructure. In 2021, it launched the world’s largest carbon market, one that already covers 12% of global CO₂ emissions. Unlike similar systems in Europe or North America that took years to gain compliance, China’s market posted a 99.5% compliance rate in its first year. Prices for carbon permits are rising steadily, signaling growing trust in the system and offering financial incentives for heavy polluters to innovate. What began with the power sector will soon expand to include industries such as cement, steel, and aviation—further embedding climate accountability into the heart of China’s industrial economy.
These efforts, while domestic in execution, carry global implications. Through the Belt and Road Initiative, China is now exporting renewable energy technology to the Global South. In African nations, Chinese-built solar systems are powering rural hospitals and schools. In Latin America and Southeast Asia, wind and hydropower projects financed by China are replacing diesel and coal. Critics may see geopolitical motives, but the environmental outcomes are real, and increasingly welcome in parts of the world where climate finance remains scarce.
At the same time, China has positioned itself as a rule-shaper on the global stage. In 2024, it revived its Voluntary Carbon Market with a focus on transparency and accountability, aligning with Article 6 of the Paris Agreement. The move strengthens China’s voice in international climate governance and reinforces its image not just as a participant in global talks, but as an architect of climate mechanisms that others now study and emulate.
Of course, challenges remain. Coal still plays a role in some regions, and energy security concerns can slow the pace of transition. But the trajectory is unmistakable. China’s path is not about overnight miracles, it is about sustained, strategic, system-wide change. And it is moving faster and more confidently than many expected.





